Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting and waterjet cutting are two major cutting processes that manufacturers commonly use when cutting material. While not always appropriate for the same applications, these two fabrication techniques offer value to manufacturing processes, albeit in different ways. To choose the right cutting method, it’s essential to understand the methods themselves and the differences between them. The point of this article is not to decide which is best between laser cutting and waterjet cutting, but to point out their differences, and to help you decide which one is best for your application.
What is Laser Cutting?
What is Waterjet Cutting?
Differences Between Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting.
What is Laser Cutting?
DefinitionA laser cutter relies on a gas laser, such as a CO2 laser, for energy. The CO2 is then transmitted through a beam, which is guided by mirrors, and directed at the material. With CO2 lasers, the laser source is located inside the machine, and the beam can output between 1500 and 2600 Watts. Materials and applications, as well as precision and safety, are important factors to think about when considering laser cutting.

Materials and Applications
Laser cutters work well with a variety of materials including, plastic, glass, wood, and all metals (except for reflective metals). If a material combination consists of materials with different melting points, however, it can be rather difficult to cut. Sandwich structures with cavities cannot be cut at all using a CO2 laser, and materials with limited access prove difficult as well. 3D material cutting is also hard to manage because of the rigid beam guidance.
Laser cutters do well with materials that range between 0.12 in and 0.4 in thickness and are commonly used to cut flat sheets of medium thickness steel. Typically, a CO2 laser cutter performs cutting, welding, drilling, engraving, ablation, and structuring.
Precision and Safety
Precision is not an issue with laser cutting, with the minimum size of the cutting slit reaching 0.006 in, depending on the speed of the laser. Thinner workpieces may suffer from gas pressure if the proper distance cannot be maintained, and partial burring does occur. Deformation and minor structural changes can occur as a result of thermal stress, and the cut material will appear striated.
Although safety goggles are not always necessary, laser cutting does produce smoke and dust, and some plastics and metals may produce toxic fumes—proper ventilation is critical. The overall risk involved in working with laser cutting machines is very low, as is the amount of waste produced and subsequent cleanup.
What is Waterjet Cutting?
DefinitionUnlike laser cutters, water jet cutters use pressurized water to cut material. To increase cutting ability, abrasives such as garnets and aluminum oxide are often added. The overall process mimics erosion in nature, just at a much higher speed and concentration: a high-pressure pump drives the water through rigid hoses, resulting in a forceful water jet—a typical water jet can output between 4 to 7 kilowatts. Unlike a laser cutter, where the laser source is located inside the machine, the work area and pump are often separate.

Water jets can cut virtually any material including combination materials—with combination materials. However, water jets pose the threat of delamination. They can sometimes handle 3D material cutting, and exhibit limited ability with sandwich structures and cavities. Cutting materials with limited access is possible but difficult.
Water jets usually perform cutting, ablation, and structuring, specifically with materials like stone, ceramics, and thick metals. Materials that range in thickness from 0.4 to 2 in benefit from water jet cutting.
Precision and Safety
Waterjet cutting is not quite as precise as laser cutting, with a minimum cut size slit of .02”. Because of the high level of force used, thin, small, parts do not fare well and must be handled carefully. Although thermal stress is not an issue and burring doesn’t occur in the cut, the surface of the material will appear sand-blasted as a result of the added abrasive to the water-jet, and goggles should be worn to protect the eyes and face. The water jet cutting process is quite noisy, and requires a significant amount of clean up—large amounts of waste occur as a result of the mixed water and abrasive.
Differences Between Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting
Operations: A laser cutting machine can engrave as well as cut material, while waterjet only allows cutting. Laser engraving is an advantage if you want to directly add serial numbers, assembly marks, or simply aesthetic designs.Waterjet cutting partially enables 3D material cutting (though it is not designed for this purpose), while laser cutting doesn’t.
As for material combinations they are also to avoid with both techniques: for laser cutting, it will pose a problem if the two materials have different melting points; for waterjet cutting, there is a danger of delamination.
To sum up, both techniques are mostly used to cut 2D objects, and laser cutting can additionally perform engraving.
The differences between these two methods don’t just lie in their methods, but in their results and applications. When choosing between laser and waterjet cutting in your applications, consider the following:
Materials and thickness: Both laser and waterjet are excellent choices to cut metals (stainless steel, steel, aluminum, copper, brass, bronze etc.). Any required secondary operations will help determine which technology is the best for the job.
Laser cutters can cut thick materials, but a waterjet machine can cut thicker objects, the optimal thickness being 0.4’’ to 2.0’’ (10 to 50 mm), while for laser cutting, it is 0.12’’ to 0.4’’ (3 to 10 mm).
Precision: Laser cutting delivers extremely high precision, reaching tolerances of +/-0.005″, depending on the speed of the laser. Waterjet cutting typically holds a tolerance of +/- 0.03″.
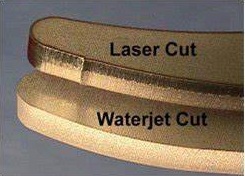
Waste: Both laser and waterjet produce little waste. Depending on the material type, there can be deburring needed with laser cutting, but very little clean up required for parts cut on the waterjet.
Tooling: Fiber laser cutting maintains a low tooling cost, since the gasses used to produce the laser and the components are inexpensive. Waterjet cutting is comparatively expensive, requiring many components to run properly, including a high-pressure pump, abrasive materials and cutting heads.
Speed: Laser cutting is capable of cutting between 50 – 2,000 inches per minute, depending on speed and material thickness, while waterjet cutting is capable of up to 100 inches per minute.
Damage on material: Each technique is posing its own problems when it comes to part integrity. Indeed, laser and waterjet machines can both damage a little the material during the manufacturing process.
Laser cutting can cause some burn marks on the material, and make the cut sides dark. In a lot of cases, the burn marks can be removed with cleaning: it’s the case for our POM material and our three laser cutting metal options. As for the darkening of the sides, it simply needs to be taken into account when thinking the design of your object: if you wish to laser cut a part in our MDF or plywood materials, for example, you can play on the contrast of colors between the colored faces and the black sides. On the contrary, our acrylic and cardboard materials won’t be marked at all.
On the other side, waterjet cutting doesn’t require heat, but it applies very high forces on the material, which can pose problems for small parts, which might get deformed, or even not be able to be cut.
In the end, each of these material fabrication methods has its own advantages and disadvantages to understand as you select your preferred method. If you need assistance deciding between custom laser cutting vs custom waterjet cutting
Risks: Laser cutting involves very low risk, waste, and required clean-up. The use of laser cutting machines doesn’t require safety goggles, even though it’s always good to wear some and be extra safe. However, for some materials, the dust and smoke produced can be slightly toxic, and it’s essential to have proper ventilation. Noise pollution is very low with laser cutting. And after the cutting process the machine doesn’t need to be heavily cleaned, as the cutting waste is mostly dust that can be vacuumed. One of the problems linked to laser cutting is the thermal stress that can occur in the heat-affected zones. To avoid thermal stress cracking, the speed can be adapted.
On the contrary, waterjet cutting involves more risks, high noise pollution, and high clean up. Indeed, the process is extremely noisy and requires ear protection. Protection is also needed against the pressured water jet (specific gears and covers, safety glasses). Moreover, the cutting area gets quite messy, with large quantities of cutting waste caused by the mixing of water and abrasives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting
AdvantagesLaser Cutting: One of the biggest reasons you might favor laser cutting is because you want to make incredibly precise cuts. If you want to laser cut steel or another metal on a very small scale, laser cutting is a great way to do it. Other cutting methods might struggle with small-scale precision cutting, but this is very easy for a laser cutter to accomplish.
Another advantage of laser cutting is that it’s able to cut through a wide variety of materials. If you need to make different kinds of cuts, you can sometimes save money by using laser cutting instead of several different cutting types.
Waterjet Cutting: One of the main advantages of waterjet cutting is the fact that it doesn’t require any heat to get results. This makes it ideal for cutting certain kinds of material for which heat would cause problems.
If you want to cut something such as plastic or certain types of metal, which would become warped or distorted due to the presence of heat, waterjet cutting is a great technique to use.
Another advantage of waterjet cutting is that it can deliver different cut edge qualities. This can be done by changing the speed of the cutting process.
If you have no specifications in mind for the cut edge, you can simply use a faster speed. If, on the other hand, you require a smoother finish on the edges, a slower speed can be used. This does mean that the edge quality impacts the expense of the job.
If you need smooth edges, you can expect the job to take longer, and therefore, it’ll cost more to run the machines.
Laser Cutting: One of the main disadvantages of using a laser cutter is that it doesn’t work very well with mixed materials. Say you have something that has a layer of wood on top of a layer of metal; a laser cutter wouldn’t really work.
This is because a laser cutter needs to achieve a specific temperature to cut certain kinds of material. Obviously, the temperature required for metal is significantly different from the temperature required for wood.
This also means that materials with multiple kinds of metal would not work too well either. Of course, the laser generates heat to get the cut, meaning it isn’t suitable for metals that might be warped by the heat.
Another factor to consider is that laser cutting can produce a lot of smoke and dust. Anyone working with or around the machine will need to wear the appropriate breathing apparatus. Failure to maintain a safe working environment could result in a lawsuit.
Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting works at its best when it’s cutting in a single concentrated area. If you introduce material such as tubing, which has a void on the inside, it can cause some problems. Cutting tubing with waterjets might result in an uneven cut.
Also, if you want to cut fibrous or stranded materials, you also might run into problems. These kinds of materials might shift around in the stream, resulting in a cut that’s uneven.
Another thing to consider is that the abrasive powder used in the jet cutting process needs to be harder than the metal the jet stream is going to cut. So, for example, if you wanted to cut tungsten using garnet powder, it’d still be possible, but the results wouldn’t really be optimal.
When using waterjet cutting, very little of the garnet powder in the water stream does any cutting. On average, if you want to do 15 minutes of cutting, you can expect to have around 30 pounds of abrasive garnet waste.
This means that the disposal of the debris is an issue. Unfortunately, it isn’t always possible to recycle this debris. Some of the garnet will become split in the process, significantly reducing its effectiveness if you were to use it again.


