Steel Forging
What is a Steel Forging? Forge Meaning? Forge definition?
Forging is a process method of using a forging machine to obtain a forged piece with certain mechanical properties, a certain shape and size. Forging and stamping are both plastic working properties, collectively called forging.
Forging is a commonly used forming method in mechanical manufacturing. Through forging, the mechanical properties of the parts are generally better than those of the same material. For the important parts with high load and severe working conditions in the machinery. In addition to the simpler shapes that can be rolled plates, profiles or welded parts, forgings are mostly used.
Forging can be divided into cold forging and hot forging.. Cold forging is generally processed at room temperature, and hot forging is processed at a temperature higher than the recrystallization temperature. In some cases, forging is performed while the temperature is still heated, but the temperature does not exceed the recrystallization temperature. This is called warm forging.
The recrystallization temperature of steel is about 460 ° C, but 800 ° C is generally used as the dividing line. Above 800 ° C is hot forging; it is called warm forging or semi-hot forging between 300 and 800 ° C.
Forging according can be divided into free forging, die forging, cold heading, radial forging, extrusion, forming rolling, roll forging, rolling and so on. The deformation of the billet under pressure is basically called free forging, which is also called open forging. The deformation of the billet in other forging methods is restricted by the die, which is called closed die forging.
Process flow
Different forging methods have different processes, wherein the hot forging process has the longest process, and the general sequence is: forging blanking; forging billet heating; roll forging stock; die forging; trimming; punching; Intermediate inspection, inspection of the dimensions and surface defects of forgings; heat treatment of forgings to eliminate forging stress and improve metal cutting performance; cleaning, mainly to remove surface oxide scale; correction; inspection, general forgings undergo appearance and hardness inspection, important forgings It is subject to chemical composition analysis, mechanical properties, residual stress and other tests and non-destructive testing.
Forging features
Compared with castings, metals can improve their microstructure and mechanical properties after forging. After the hot-working deformation of the cast structure by the forging method, the original coarse dendrites and columnar grains become the equiaxed recrystallized structure with fine grains and uniform size due to the deformation and recrystallization of the metal, so that the original segregation in the steel ingot, The compaction and welding of loose, stomata and slag inclusions make the structure more compact and improve the plasticity and mechanical properties of the metal.
1. Free forging
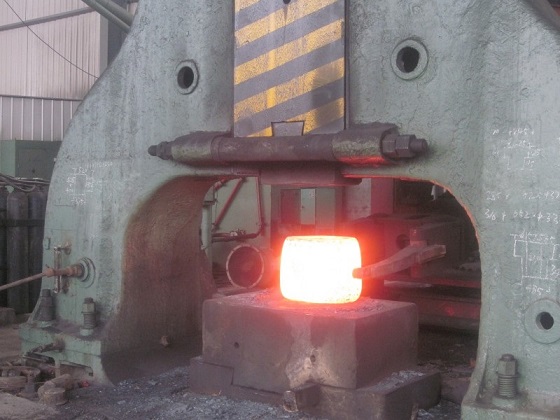

Free forgings are not high in precision and simple in shape. Their shape and size are generally guaranteed by the operator using general-purpose tools, mainly for single-piece and small-batch production. For the manufacture of large machine forgings, free forging is still the only effective method. Free forging has high technical requirements for the blacksmith, poor working conditions and low production efficiency. Forgings that require only a simple universal tool or directly deform the billet between the upper and lower anvils of the forging equipment to obtain the required geometry and internal quality are called free forging.
1. The basic process can be divided into drawing, upsetting, punching, bending。
Drawing length: Also called extension, it is a forging process that reduces the cross-sectional area of the billet and increases the length.
Upsetting: a forging process that reduces the height of the blank and increases the cross-sectional area.
Punching: It is a forging method that uses a punch to punch through or through holes on the blank after upsetting.
Bending: A forging process that bends the blank into a prescribed shape using a certain tooling.
2. Features and applications of free forging
Features: greater process flexibility and shorter production preparation time;The productivity is low, the accuracy of forgings is not high, and forgings with complex shapes cannot be forged.
Application: Free forging is the main production method of large forgings. This is because free forging can break the coarse casting structure in the steel ingot, forge the voids and shrinkage inside the steel ingot, and make the streamlined structure reasonable distribution along the shape of the forging.
2. Die forging


Die forging refers to a forging method in which a blank is molded by a mold on a special die forging device to obtain a forged piece. The forgings produced by this method are accurate in size, have a small machining allowance, and have a relatively complicated structure and productivity. According to the different classification of equipment used: hammer forging, crank press forging, flat forging machine forging and friction press forging. The most commonly used equipment for hammer forging is steam-air die forging hammer, and Anyang forging has achieved high achievements in the domestic die forging full hydraulic field without anvil hammer and high speed hammer.
Abbreviated as forging, it is a forging method to obtain forgings by deforming the blank with a die (forging die) on a die forging outward hammer.
Features: Compared with free forging and tire die forging, it has the following advantages
① High production efficiency
② The surface quality is high, the machining allowance is small, there are few or no surplus pieces, the size is accurate, the tolerance of the forging is 2/3 ~ 3/4 smaller than that of the free forging, which can save a lot of metal materials and machining man-hours.
③ Simple operation and lower labor intensity than both free forging and tire die forging.
Disadvantages:
① The weight of die forgings is limited by the capacity of general die forging equipment, and most of them are below 50 ~ 70kg;
② Forging dies require valuable die steel, and the processing of the die cavity is difficult, so the manufacturing cycle of forging dies is long and the cost is high;
③ The investment cost of die forging equipment is greater than that of free forging.
Application: Generally used for producing large quantities of forgings.
Forging materials are mainly carbon steel and alloy steel with various components, followed by aluminum, magnesium, copper, titanium, and their alloys. The original state of the material is bar, ingot, metal powder and liquid metal.
General small and medium-sized forgings use round or square bar stock as the blank. The grain structure and mechanical properties of the bar material are uniform and good, the shape and size are accurate, and the surface quality is good, which is convenient for mass production. As long as the heating temperature and deformation conditions are reasonably controlled, forgings with excellent performance can be forged without major forging deformation.
Ingots are only used for large forgings. The ingot is a as-cast structure with large columnar crystals and loose centers. Therefore, it is necessary to break the columnar crystals into fine grains through large plastic deformation and compact and loosen them to obtain excellent metal structure and mechanical properties.
The powder metallurgical preforms that are pressed and sintered can be made into powder forgings by flashless die forging in the hot state. The density of forging powder is close to the density of general forgings, has good mechanical properties, and has high precision, which can reduce subsequent cutting processing. The internal structure of powder forgings is uniform, without segregation, and can be used to manufacture small gears and other workpieces. However, the price of powder is much higher than that of ordinary bars, and its application in production is limited.
By applying static pressure to the liquid metal poured into the mold cavity, it can be solidified, crystallized, flowed, plastically deformed and formed under pressure to obtain a forged piece with the required shape and performance. Liquid metal die forging is a forming method between Die casting and die forging. It is especially suitable for complex thin-walled parts that are difficult to form in general die forging.
Different forging methods have different processes. Among them, the hot forging process is the longest. The general sequence is: blank forging; heating of the forging; heating forging by rolls; forming by die forging; trimming; intermediate inspection and inspection of forgings Dimensions and surface defects; heat treatment of forgings to eliminate forging stress and improve metal cutting performance; cleaning, mainly to remove surface oxide scale; correction; inspection, general forgings are subject to appearance and hardness inspection, and important forgings also undergo chemical composition analysis , Mechanical properties, residual stress and other inspections and non-destructive testing.
Forging is the collective name of forging and stamping. It is a forming method that uses the hammer, anvil, punch of a forging machine or a die to apply pressure to the blank to plastically deform it to obtain the desired shape and size. .

In the forging process, the billet as a whole undergoes significant plastic deformation and has a large amount of plastic flow. In the stamping process, the billet is mainly formed by changing the spatial position of the area of each part, and the plastic flow does not occur within a large distance. Forging is mainly used to process metal parts, and it can also be used to process certain non-metals, such as engineering plastics, rubber, ceramic billets, brick billets, and composite materials.
Rolling and drawing in the forging and metallurgical industries are all plastic processing, or pressure processing, but forging is mainly used to produce metal parts, while rolling and drawing are mainly used to produce sheet, strip, pipe, Universal metal materials such as profiles and wires.
Forging is mainly classified by forming method and deformation temperature. Forging according to the forming method can be divided into forging and stamping; forging according to the deformation temperature can be divided into hot forging, cold forging, warm forging and isothermal forging.
Hot forging is a forging that is performed above the metal recrystallization temperature. Increasing the temperature can improve the plasticity of the metal, which is conducive to improving the inherent quality of the workpiece and making it difficult to crack. High temperature can also reduce the deformation resistance of the metal and reduce the tonnage of the required forging machinery. However, there are many hot forging processes, the accuracy of the workpiece is poor, the surface is not smooth, and the forging is prone to oxidation, decarburization and burnout.
Cold forging is a forging at a temperature lower than the recrystallization temperature of the metal. Generally speaking, cold forging refers to the forging at room temperature, and the forging at a temperature higher than normal but not exceeding the recrystallization temperature is called temperature Forging. The precision of warm forging is higher, the surface is smoother and the resistance to deformation is small.
Cold-forged workpieces at room temperature have high shape and dimensional accuracy, a smooth surface, and fewer processing steps, which is convenient for automated production. Many cold forged and cold stamped parts can be used directly as parts or products without cutting. However, during cold forging, due to the low plasticity of the metal, cracks are easy to occur during deformation, and the deformation resistance is large, requiring large tonnage forging machinery.
Isothermal forging is a process in which the billet temperature remains constant throughout the forming process. Isothermal forging is to make full use of the high plasticity of certain metals at an isothermal temperature, or to obtain specific microstructures and properties. Isothermal forging requires the mold and the blank to be kept at a constant temperature, which requires higher costs, and is only used for special forging processes, such as superplastic forming.
Forging can change the metal structure and improve the metal properties. After the ingot is hot-forged, the original as-cast looseness, porosity, and microcracking are compacted or welded; the original dendrite is broken to make the grains finer; at the same time, the original carbide segregation and unevenness are changed Distribution, make the organization uniform, so as to obtain a dense, uniform, fine, comprehensive performance, reliable forgings. After the hot forging is deformed, the metal is a fibrous structure; after cold forging, the metal crystals are in order.
Forging is a process in which metal is plastically flowed into a desired shape. The volume of the metal does not change after plastic flow due to external force, and the metal always flows to the part with the least resistance. In production, the shape of the workpiece is often controlled according to these rules to achieve deformation such as upsetting, drawing, reaming, bending, and drawing.
The size of the forged workpiece is accurate, which is conducive to the organization of mass production. Die forging, extrusion, stamping and other application mold forming dimensions are accurate and stable. It can use high-efficiency forging machinery and automatic forging production line to organize specialized mass production or mass production.
The production process of forging includes the forging billet blanking, forging billet heating and pretreatment before forming; the heat treatment, cleaning, calibration and inspection of the workpiece after forming. Common forging presses are forging hammers, hydraulic presses, and mechanical presses. The forging hammer has a large impact speed, which is conducive to the plastic flow of metal, but it will produce vibrations. The static forging of the hydraulic press is conducive to forging through the metal and improving the organization. The work is stable but the productivity is low. The fixed stroke of the mechanical press is easy to realize mechanization And automation.
In the future, the forging process will improve the inherent quality of forgings, develop precision forging and precision stamping technology, develop forging equipment and forging production lines with higher productivity and automation, develop flexible forging forming systems, develop new forging materials and methods. development of.
Improving the intrinsic quality of forged parts is mainly to improve their mechanical properties (strength, plasticity, toughness, fatigue strength) and reliability. This requires better application of metal plastic deformation theory; application of materials with better internal quality; proper pre-forging heating and forging heat treatment; stricter and more extensive non-destructive testing of forged parts.
Less and no cutting is the most important measure and direction for the machinery industry to improve material utilization, improve labor productivity and reduce energy consumption. Less forging billet, non-oxidizing heating, and the development of high-hardness, wear-resistant, long-life mold materials and surface treatment methods will be conducive to the expansion of precision forging and precision stamping applications.
Forge Meaning, forge definition: It is one of the two major components of forging (forging and stamping) by using a forging machine to apply pressure to a metal blank to plastically deform it to obtain a forging with certain mechanical properties, a certain shape and size. Casting: A method in which liquid metal is cast into a casting cavity that conforms to the shape of the part and is cooled and solidified to obtain a part or blank.
Forging: A method of hammering or the like to make a metal material in a plastic state into a workpiece having a certain shape and size, and changing its physical properties. Casting: A method in which a metal is melted into a liquid, poured into a mold, cooled and solidified, and cleaned to obtain a casting of a desired shape. Can be made into a variety of shapes and shapes of objects.
Forging is generally used in the processing of forgings of a certain shape and size. Casting is a relatively economical method of forming blanks and is generally used on parts with complex shapes.
Deshengrui have rich experience with steel forging and aluminum forging.When you have technical difficulty, you can come to us with more support.Vist our website: www.desheng-precision.com for more details.


